
As for a guitarist, it’s so common to hear many guitar-specific terms and not understand what it actually means.
For a beginner, it is very important that you know at least a few of them. With these key terminologies in hand, Learning to play your guitar will be very easy.
Just make sure to bookmark this page and keep it as a reference so you can visit back at any time. Don’t worry, it’s going to be easy learning.
I have listed below the glossary of all the common terms you will often hear when learning and watching tutorials of playing guitars.
So, let’s begin!
Terminologies of Guitars Parts
All the guitars have the same guitar parts names even irrespective of whether it’s acoustic, electric or bass guitars.
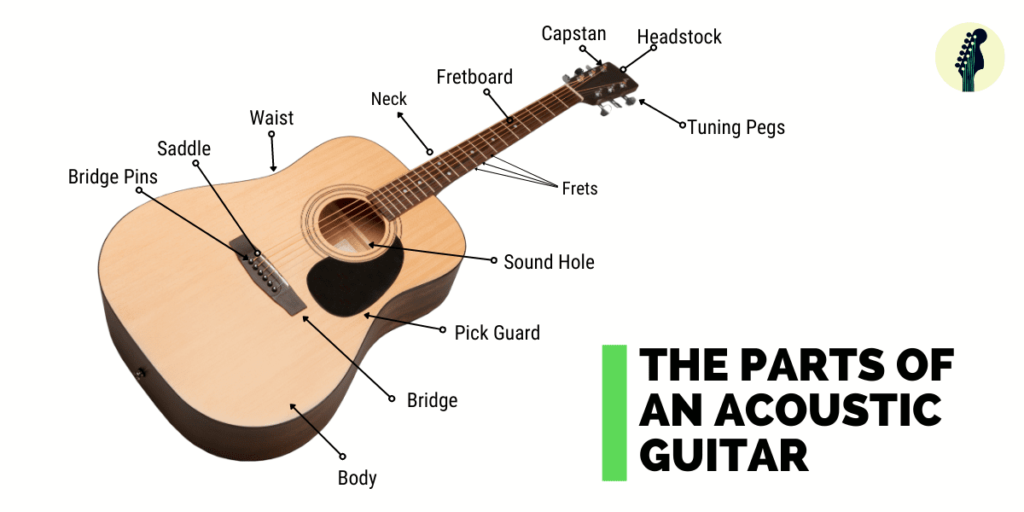
- Fretboard – The fretboard is the narrow area over which the strings run over. It’s on the front of the neck of the guitar. You can also refer it to as the area between the nut and bridge.
- Fret – The frets are the singly divided sections on the fretboard which is referred to by numbers – 1st fret, 2nd fret, and so on.
- Neck – The middle, narrow section of the guitar is referred to as the neck of the guitar.
- Tuning Pegs – Tuning pegs are the cylindrical knob-like structure at the top-most of your guitar, when turned tightens and loosens the guitar strings. It’s essential to have a good tuning peg to keep the guitar strings right and tight in condition. You obviously don’t want the strings to loosen up and go off-tune while you are playing your masterpiece music.
- Strings – They are thick and thin wires running straight across the guitar from the bridge to inside the tuning pegs. The guitars have a special guitar string naming convention. We count the strings from right to left and number them as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6th string. As for the standard tuning we follow – EADGBE is the order (from left to right) to which we tune each of our strings.
- Bridge – The bridge is the most important part of a guitar. It supports the strings on a guitar and transmits the vibration to the soundboard. As normal as it may seem, the strings on the guitar alone can’t produce large sound output. This is where the soundboard, under the bridge help in making the sound louder.
- Single Coil – A single-coil is a pickup that detects and responds to the vibrations of the strings, amplified and finally tuned to sound.
It’s used mostly in electric and electrical bass guitars. - Pickups – A pickup is the most important part of an electric guitar. It is used to convert the string vibrations to electricity and is placed just below the strings.
- Toggle Switch – It’s a switch used to select pickups. Normally we say it switches between neck pickup, mid pickup, and bridge pickup. You can move it to adjust the sound from warmer on top to sharper at the bottom.
- Headstock – This is common to all string musical instruments and found on the head of the guitar. It’s where you have tuning pegs to adjust the tension in the strings, and thus changes the sound pitch they produce.
- Bridge Pins – Bridge pins are the small pegs seen on the guitar bridge. It connects the other end of the strings bridge plate hidden inside the body. In brief, It has small sound effects on the strings due to damping.
Terminologies in Guitar Sound
- Bass – It refers to a “deep” low-frequency sound or a low pitch sound.
- Flat – Any sound that is played through a monitoring system and sounds exactly like the source without much variation is called a flat sound.
- Harmony – It when two or more different sounds or notes are played together or simultaneously.
- Melody – Successive notes that make sounds that are pleasant to hear.
- Natural – Sounds that are naturally made.
- Octave – The word origins from a Latin root meaning “eight”. It means an interval whose higher note has a sound-wave frequency of vibration twice that of its lower note.
For example, C major scale is a diatonic scale – “C D EF G A BC…” The repetition of C at the second time vibrates twice as fast as the first is at an octave higher. - Pitch – Pitch refers to the quality of sound. It is the most important term in music, especially singing. It’s a frequency-related scale which means a high pitch sound corresponds to a high-frequency sound.
- Reverb – It’s the effect of decaying reflections of sounds off of multiple surfaces heard after the initial sound source. You can understand this much better with a good video example.
- Rhythm – The movement/flow of sound in a regular pattern or interval.
- Riff – A riff is a short repeated tune, a commonly used term in jazz music.
- Tremolo – It is the volume or amplitude-based alteration to the note. It’s often compared with Vibrato. However, vibrato deals with change in pitch and Tremolo with volume change.
- Scale – A scale is simply a way of ordering the twelve sounds found in Western Music. For beginners, we had listed the easiest beginner-friendly scales to must know.
- Sharp – A strong sound piercing sound easy to distinguish from others. Technically it means – “higher in pitch by one semitone (half step)”.
- Treble – This corresponds to “high notes” in music, which goes to higher-end frequencies that humans can hear.
- Tempo – It basically refers to the speed of musical beats. The higher the tempo, the faster the music gets to feel playing.
- Tone – A tone is a certain frequency at which you hear a sound. It has a specific quality and has only a single frequency.
Basic Guitar Terms & Slangs
- Action – It refers to the height of the string from the fretboard.
- Alternate Picking – Refers to alternating downward and upward strokes
- Alternate Tunings – It refers to having a guitar tuned differently from standard tuning. This is not intended for beginners or intermediates.
- Fingerstyle – Fingerstyle is the technique of playing the guitar by plucking the strings directly or with the fingertips/fingernails.
- Vibrato – It literally meaning is – “to shake”. It involves doing movements like bending, pushing, pulling a particular note. You can check the vibrato lesson here.
- Beat – It refers to a small time frame in music that’s usually associated with rhythmic patterns.
- Bend – A string bend is when you bend the string across the same fret to create a special sound effect.
- BPM – It expands to Beats Per Minute (bpm). Hence a 1 beat/second music will correspond to 60 bpm.
- Note – They are the smallest unit of musical language.
- Chord – The Notes in a music group together to form Chords.
- Chord Diagram – It’s a six vertical line figure corresponding to strings of a guitar that tell you the finger placements for each chord.
- Compressor – A compressor is a special accessory connected to the signal output of the guitar to change the overall sound dynamics. They are commonly used by bass guitarists.
- Delay – The delay is a sound effect added to replicate the sound after a certain delay. Its commonly done by digital methods these days.
- Modes – In simple terms, modes are scales derived from a parent scale.
- Modulation – It refers to varying one or more properties of sound in a guitar.
- Diatonic – Diatonic scales which are seven notes long are used in Western music. The eighth note in the diatonic scale is considered a repetition of the first but at a higher pitch.
- Distortion – Any “fuzzy” or “unwanted” sound, usually used in rock music by increasing the gain of the sound.
- Tab/Tablature – Its method of writing down guitar played notes using a different notation, unlike standard musical notation. It helps any guitarist to read and play songs they wish to play.
- Strumming – Striking/Playing several strings together is called guitar strumming.
- Downstroke – The downwards strumming is called downstroke.
- Upstroke – The upwards strumming is called upstroke.
- Dynamics – The change in fluidity of sound – from loud to quiet and vice versa refers to dynamics of sound.
- Picking – It means to pick/strum only an individual string.
- Intonation – It’s the extent to which the notes formed are in pitch or in tune. It basically looks forward to the accuracy of pitch sound.
- Open String – The string that is played without your hands on it is called an open string.
- Major Chord – A major chord consists of a 1st, 3rd, and 5th degree of a major scale. This adds in bright, enlightening musical sounds.
- Minor Chord – A minor chord consists of 1st, flatted 3rd, and 5th degrees of a major scale, which feels like sad or heartbroken sounds.
- Barre chord – A barre chord (also spelled bar chord) is a type of chord on any stringed instrument, that is played by using one or more fingers pressed down on multiple strings across the same single fret.
- Suspended Chord – This chord acts like a substitution chord, which is useful when some chords are hard to reach and play.
- Pentatonic Scale – A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave. As compared to a major or minor scale, they do sound somewhat different.
- Power Chord – It is a two-note chord, with no major or minor quality to it. They are made up of the root and fifth of the chords.
- Triad – A triad is a group of three notes that are all a 3rd apart. For example, the C major triad is made up of C (root), E (major third), and G (perfect fifth).
- Triplet – Three notes played in succession, per beat is called a Triplet.
- Sustain – It’s the time a particular note resonates.
- Slide – As it literally means, it slides across the same string to add to a damping sound effect.
- Pull-offs – Pull-offs allow us to play two or more notes with just one pick. When playing a note, release the fretting finger, and passing it to a finger just down the neck creates this effect.
- Hammer-on – This is just opposite to Pull offs. Here the note is played and without lifting, the finger is placed just down the next to create more notes with the single pick.
- Chucking – Its a technique with acoustic guitar, where open strums and dead note “chucks” are alternated to create a rhythmic pattern
- Interval – Space between any two pitches is called an Interval.
- Lick – It refers to short series of notes that is used in solos which is a part of the song.
Terminologies of Guitar Accessories
- Strap Locks – It helps the guitar stay secure and comfortable to prevent it from falling off.
- Strap – Guitar straps as evidently means are straps that run over your shoulder to keep the guitar to you while playing.
- Finger Picks/ Plectrums – Finger picks are used mainly in the fingerstyle technique, to pluck and play strings individually. As you get used to the fingerpicks, you’ll sound better and have more control. But then, not everyone likes using finger pricks. It’s up to you!
- EQ – It is a sound engineering tool that adjusts the output of different frequencies.
- Capo – A capo is used in guitar to manipulate the overall tone of the guitar. It used to raise the pitch of a fretted instrument.
- Pedal/Effects Pedal/Stompbox – A stompbox is a small box placed under the foot, which is tapped or stamped on rhythmically to produce a sound similar to that of a bass drum.
- Tuner – Guitar tuners are used to adjust the frequency of the strings to the perfect pitch required.
- Amplifier (Amp) – Guitar amplifiers are used to amplify the sounds to reach the guitar sounds to a larger distance.
- Audio Interface – Audio interface is a device that’s used to monitor and control different IO ports and recording devices that connects your guitar to the recording system.
Conclusion
Even though all of the accessories, guitar terms and slangs might not come useful to beginners now, Its always good to know these stuff.
If you have more guitar slangs to share, do share in the comments below. I would love to include it in the list.

Leave a Reply